Gout
Gout
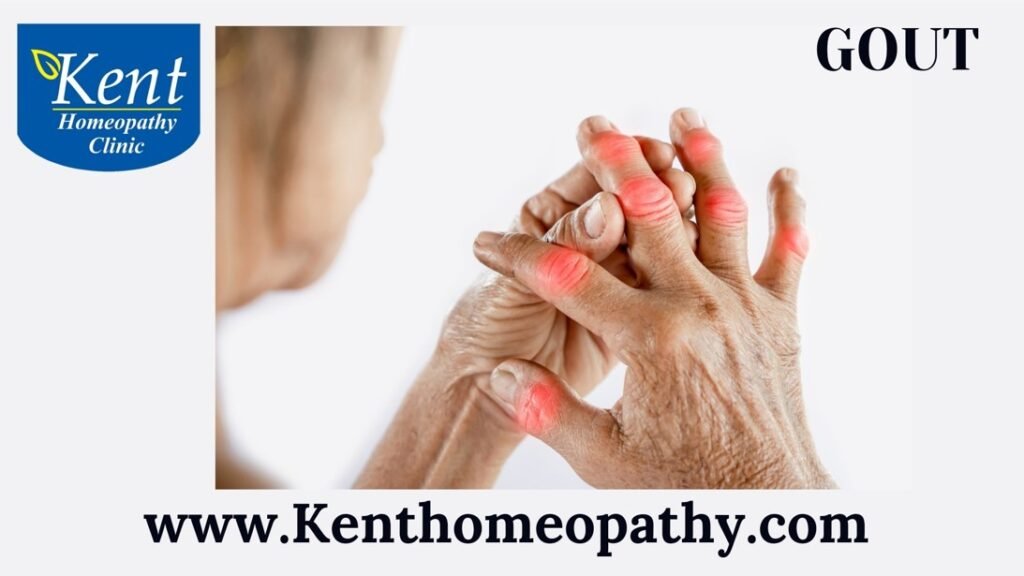
Gout is a type of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints, typically the base of the big toe. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints and surrounding tissues. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of gout is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Symptoms:
Gout symptoms can manifest suddenly and often occur at night. Common signs include:
- Intense Joint Pain: Typically affecting the big toe, gout attacks cause sudden and severe pain in the affected joint. Other joints like ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers may also be affected.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint becomes swollen, red, and warm to the touch due to inflammation.
- Limited Range of Motion: Joint stiffness and difficulty moving the affected joint may occur during and after an attack.
- Tophi Formation: In chronic gout, the repeated inflammation can lead to the development of tophi, which are urate crystal deposits visible under the skin.
Causes:
Gout is primarily caused by an accumulation of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of sharp urate crystals in the joints. The main contributing factors include:
- Overproduction of Uric Acid: The body produces too much uric acid, often due to genetic factors or certain medical conditions.
- Impaired Uric Acid Excretion: The kidneys are unable to efficiently remove uric acid from the body, leading to its buildup.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake, especially beer, has been associated with an increased risk of gout.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the risk of gout as excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels.
- Certain Medications: Diuretics and medications that interfere with uric acid excretion can contribute to gout.
Types:
- Acute Gout: Characterized by sudden and intense pain, swelling, and redness during gout attacks.
- Chronic Gout: Recurrent gout attacks over an extended period can lead to chronic gout, with the potential development of tophi and joint damage.
- Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia: Some individuals have elevated uric acid levels without experiencing gout symptoms. However, they may be at risk of developing gout in the future.
- Recurrent Gout: Individuals who experience multiple gout attacks over time fall into this category.
Contact to know more
Contact
Powai: 52, Galleria Mall,
Central Avenue, Hiranandani Gardens,
Powai, Mumbai-400076
Mobile Number: 08291492566
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
