Fungal infection
Fungal Infection:
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by various types of fungi and can affect different parts of the body. These infections can range from mild to severe, and symptoms may vary based on the type of fungus and the affected area.
Symptoms:
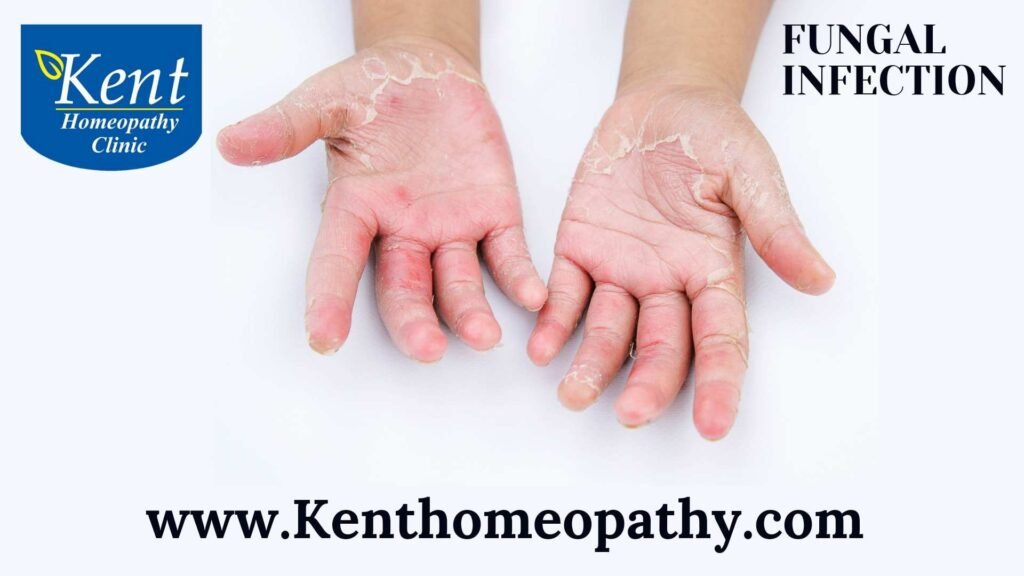
- Skin Infections:
– Itching and redness on the skin.
– Formation of rashes or blisters.
– Peeling or cracking of the skin.
– Fungal infections like athlete’s foot or ringworm commonly affect the skin.
- Nail Infections:
– Thickening, discoloration, or deformation of nails.
– Brittle or crumbly nails.
– Fungal nail infections often affect toenails and fingernails.
- Oral Infections:
– White patches in the mouth or on the tongue (oral thrush).
– Soreness and difficulty swallowing.
– Fungal infections like candidiasis can impact the mouth and throat.
- Genital Infections:
– Itching, redness, and discomfort in the genital area.
– Abnormal vaginal discharge in women.
– Fungal infections like yeast infections commonly affect the genital region.
- Systemic Infections:
– Fever and chills.
– Respiratory symptoms if the infection spreads to the lungs.
– Systemic fungal infections can be severe and affect internal organs.
Causes:
- Fungal Species: Different fungi, including yeasts and molds, can cause infections. Common culprits include Candida, Aspergillus, and dermatophytes.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Environmental Exposure: Fungi thrive in warm and humid environments. Exposure to contaminated soil, water, or surfaces can contribute to infections.
- Poor Hygiene: Lack of proper hygiene, especially in moist areas like skin folds, can create an environment conducive to fungal growth.
- Use of Antibiotics: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body, allowing fungi to proliferate.
Types:
- Superficial Infections:
– Cutaneous Infections: Affect the skin, hair, or nails. Examples include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and nail infections.
– Mucocutaneous Infections: Involve both the skin and mucous membranes, such as oral thrush.
- Subcutaneous Infections:
– Extend into the deeper layers of the skin and tissues. These infections are less common and may result from traumatic injuries. Examples include sporotrichosis.
- Systemic Infections:
– Involve internal organs and can be life-threatening. Examples include invasive candidiasis and aspergillosis.
- Opportunistic Infections:
– Occur in individuals with weakened immune systems. Fungi that are normally harmless can cause infections in these cases. Examples include cryptococcosis in HIV/AIDS patients.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
