Bedbug Bites
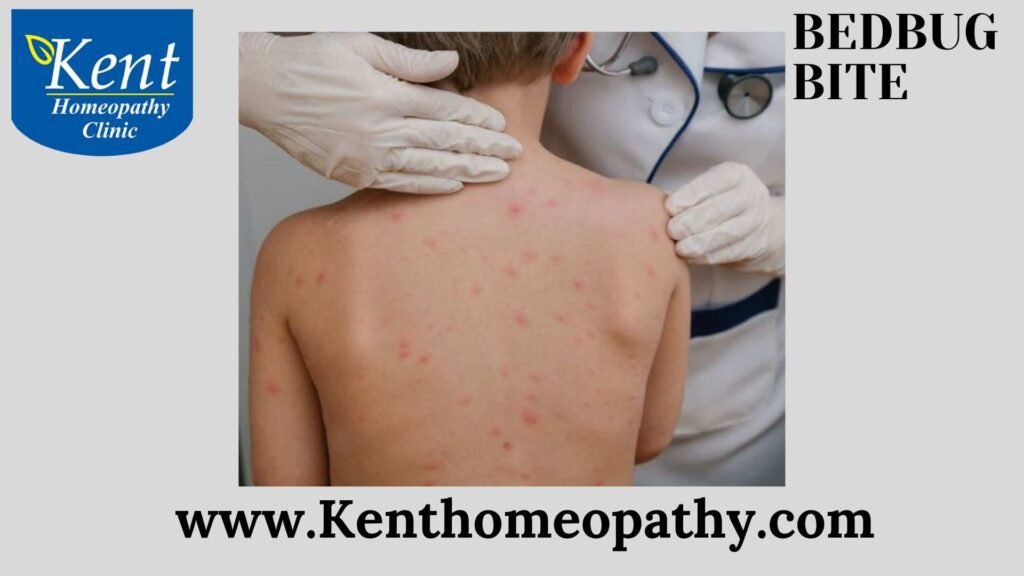
Bedbug bites are skin reactions resulting from the bites of bedbugs (Cimex lectularius). These small, reddish-brown insects feed on the blood of humans and animals during the night. While bedbugs are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can cause discomfort and skin reactions in some individuals. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of bedbug bites can help in identifying and managing these bites.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of bedbug bites can vary from person to person, and not everyone reacts to bedbug bites in the same way. Common symptoms include:
- Red, Itchy Bumps: Bedbug bites typically appear as small, red bumps on the skin. They are often itchy and can be grouped together in a line or cluster.
- Swelling: The affected area may become swollen due to the body’s inflammatory response to the bites.
- Red or Dark Spots: Some individuals may develop red or dark spots in the center of the bite marks. These spots can result from the bedbug’s feeding process.
- Itching: Bedbug bites are known for causing itching, which can range from mild to intense. Excessive scratching can lead to secondary infections.
- Linear or Clustered Pattern: Bedbug bites often appear in a linear or clustered pattern, as bedbugs tend to bite multiple times in close proximity.
It’s important to note that while bedbug bites share some similarities with other insect bites, they do not have a distinctive appearance, making it challenging to diagnose based solely on the appearance of the bites.
Causes:
The primary cause of bedbug bites is the feeding behavior of bedbugs. Bedbugs are nocturnal insects that feed on blood by piercing the skin with their mouthparts and withdrawing blood for several minutes. The causes of bedbug bites include:
- Bedbug Feeding: Bedbugs are attracted to the warmth and carbon dioxide emitted by humans, making them more active during the night. They typically bite exposed areas of skin while individuals are asleep.
- Infestation: Bedbug bites occur when there is a bedbug infestation in the sleeping or resting area. Bedbugs hide in cracks, crevices, and furniture during the day and come out at night to feed.
- Travel or Infested Environment: Individuals may experience bedbug bites after staying in infested accommodations, using infested furniture, or residing in an environment with a bedbug infestation.
- Clothing or Luggage Infestation: Bedbugs can also infest clothing, bedding, and luggage, allowing them to be transported to new locations. Bites may occur when the infested items are used or unpacked.
- Lack of Awareness: Bedbug bites may go unnoticed initially, and individuals may not realize they are being bitten until an infestation has progressed.
Types:
While bedbug bites themselves do not have distinct types, the reactions and severity of symptoms can vary among individuals. Some people may not react at all to bedbug bites, while others may experience more pronounced symptoms. Types of reactions to bedbug bites include:
- 1. Mild Reactions: Some individuals may have mild or no reactions to bedbug bites. They may not experience significant itching or swelling, making it difficult to detect the presence of bedbugs.
- Localized Reactions: Many people experience localized reactions, characterized by red, itchy bumps in the bitten area. The itching may be bothersome but usually resolves without severe complications.
- Allergic Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may be allergic to components in bedbug saliva, leading to more severe allergic reactions. These reactions may include widespread hives, difficulty breathing, or anaphylaxis, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Secondary Infections: Excessive scratching of bedbug bites can break the skin, increasing the risk of secondary bacterial infections. Infected bites may become red, swollen, and painful, requiring medical treatment.
It’s important to distinguish between bedbug bites and bites from other insects or skin conditions. Bedbug bites are not known to transmit diseases, but their presence can cause psychological distress and disrupt sleep. If an individual suspects bedbug bites or encounters signs of a bedbug infestation, it is advisable to seek professional pest control services for thorough inspection and treatment.
Managing bedbug bites involves avoiding excessive scratching to prevent secondary infections. Over-the-counter creams or antihistamines can help alleviate itching and inflammation. In cases of severe allergic reactions or secondary infections, medical consultation is recommended.
Preventing bedbug bites involves taking measures to avoid infestations, such as regularly inspecting and cleaning sleeping areas, using protective covers on mattresses and pillows, and being cautious when staying in unfamiliar accommodations. If there is concern about bedbug bites or an infestation, consulting with a healthcare professional or a pest control specialist is recommended for appropriate guidance and intervention.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
