Eczema
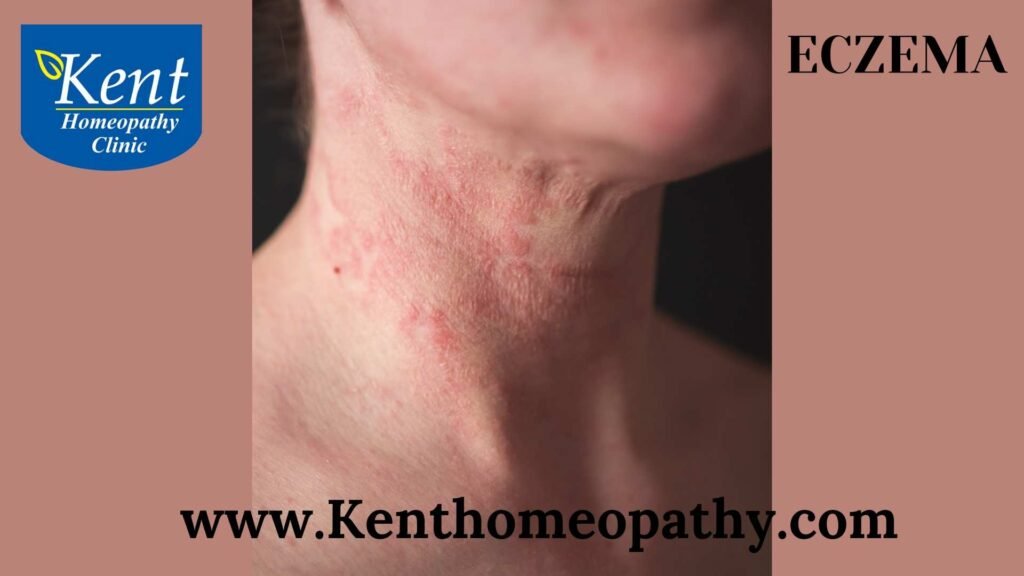
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often begins in childhood but can affect individuals of any age. Eczema is not contagious, and while there is no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms.
Symptoms:
- Itching: Intense itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema, and scratching can worsen the condition.
- Red or Inflamed Skin: Areas of the skin affected by eczema may appear red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Dry or Cracked Skin: The affected skin often becomes dry, and in severe cases, it may crack, leading to increased vulnerability to infections.
- Blisters or Oozing Lesions: In some cases, eczema can cause the formation of small blisters or oozing lesions, especially during flare-ups.
- Thickened Skin: Prolonged scratching or rubbing can lead to thickened, leathery skin, known as lichenification.
Causes:
- Genetics: There is a strong genetic component to eczema, and individuals with a family history of atopic conditions (eczema, asthma, hay fever) are more predisposed.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Eczema is linked to an overactive immune response, causing inflammation in the skin.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, or certain fabrics can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Allergens: Allergens like pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods can trigger or worsen eczema in some individuals.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: Individuals with eczema often have a compromised skin barrier, allowing irritants to penetrate more easily and moisture to escape, leading to dryness.
Types:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form of eczema, atopic dermatitis often begins in childhood and is associated with a family history of atopic conditions.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type is triggered by contact with irritants or allergens. It can be further classified into irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
- Nummular Eczema: Characterized by coin-shaped patches of irritated skin, nummular eczema may be linked to dry skin and environmental factors.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Often affecting the scalp and face, seborrheic dermatitis is associated with red, scaly, and oily skin. It can occur in infants as cradle cap.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: This type involves the formation of small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, and is often triggered by stress or exposure to certain metals.
Individuals with eczema should work closely with dermatologists to develop a personalized treatment plan. While there is no cure, effective management strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those with eczema.
Contact to know more
Contact
Powai: 52, Galleria Mall,
Central Avenue, Hiranandani Gardens,
Powai, Mumbai-400076
Mobile Number: 08291492566
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
