Hirsuitism
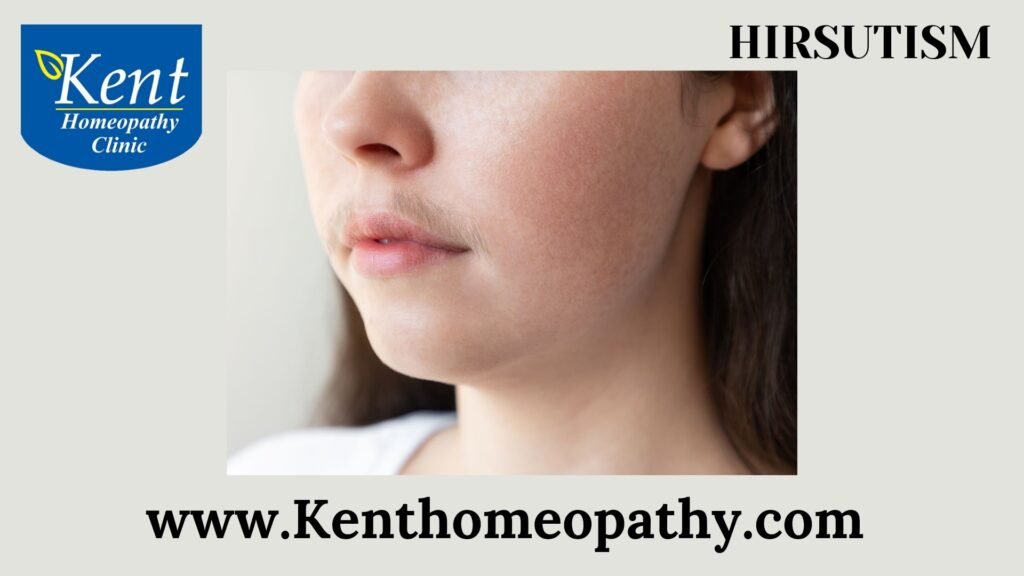
Hirsutism: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Types
Hirsutism is a condition characterized by the excessive growth of coarse, dark hair in areas where hair growth is typically associated with male patterns. This includes areas such as the face, chest, back, and abdomen in women. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of hirsutism is crucial for diagnosis and appropriate management.
Symptoms:
The primary symptom of hirsutism is the development of excess hair in areas where women typically have fine or no visible hair growth. Common areas affected include the:
- Face: Growth of coarse, dark hair on the upper lip, chin, and cheeks.
- Chest: Presence of hair on the chest, which may extend towards the abdomen.
- Back: Development of coarse hair on the upper and lower back.
- Abdomen: Hair growth in the abdominal region, particularly around the navel.
Causes:
Hirsutism can result from various factors, and its underlying causes include:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal disorder in women where an imbalance in reproductive hormones can lead to hirsutism.
- Idiopathic Hirsutism: In some cases, the cause of hirsutism may not be readily apparent, and it is classified as idiopathic.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as anabolic steroids or certain hormonal treatments, can contribute to increased hair growth.
- Adrenal Gland Disorders: Conditions affecting the adrenal glands, such as adrenal tumors or congenital adrenal hyperplasia, can lead to hirsutism.
- Cushing’s Syndrome: A disorder characterized by excess production of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands.
- Genetic Factors: Hirsutism can sometimes run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Tumors: Rarely, tumors affecting the ovaries or adrenal glands may produce hormones that trigger hirsutism.
Types:
Hirsutism is often classified based on its cause and severity:
- Idiopathic Hirsutism: Hirsutism with no apparent underlying cause.
- PCOS-Related Hirsutism: Associated with polycystic ovary syndrome and hormonal imbalances.
- Drug-Induced Hirsutism: Resulting from the use of medications that influence hormonal levels.
- Tumor-Induced Hirsutism: Caused by tumors that produce excess hormones leading to hirsutism.
Hirsutism is a condition that may impact self-esteem, and individuals experiencing excessive hair growth should seek medical advice for a thorough evaluation. Treatment plans are often tailored to address the underlying cause and manage symptoms effectively.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
