Impetigo
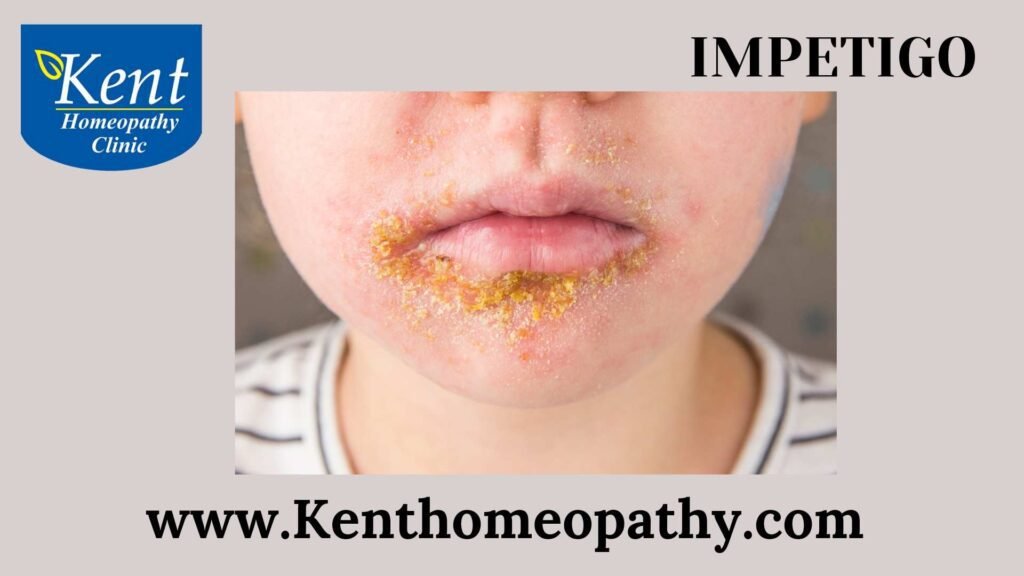
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection caused by bacteria, primarily Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It is more common in children than adults and is characterized by the development of red sores or blisters on the skin, often around the nose and mouth. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of impetigo is crucial for accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment.
Symptoms:
- Red Sores: The primary symptom of impetigo is the presence of red sores that quickly turn into blisters. These blisters may ooze and form a yellowish-brown crust.
- Itching: The affected area may be itchy, and scratching can contribute to the spread of the infection.
- Rash: The rash associated with impetigo can be widespread, and it may start as small red spots that evolve into larger blisters.
- Fluid-filled Blisters: The blisters may contain fluid that can spread the infection to other parts of the body or to other people through direct contact.
- Honey-Colored Crusts: As the blisters rupture, they leave behind a characteristic honey-colored crust. This crust is a key feature in distinguishing impetigo from other skin conditions.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: In some cases, nearby lymph nodes may become swollen as the body responds to the bacterial infection.
Causes:
- Bacterial Infection: Impetigo is caused by bacteria, with Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes being the most common culprits. The bacteria enter the skin through cuts, scratches, or insect bites, initiating the infection.
- Poor Hygiene: Lack of proper hygiene, especially in crowded or unsanitary conditions, can increase the risk of impetigo.
- Skin Injuries: Any break in the skin, such as cuts, abrasions, or insect bites, provides an entry point for bacteria, increasing the likelihood of impetigo.
- Close Contact: Impetigo is highly contagious, and it can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. Sharing personal items, such as towels or razors, can also contribute to the transmission of the bacteria.
- Warm and Humid Environment: Bacteria thrive in warm and humid environments, making these conditions conducive to the development and spread of impetigo.
Types:
- Non-bullous Impetigo: This is the most common form of impetigo. It typically begins as small red sores that quickly progress to fluid-filled blisters. As the blisters rupture, they form a characteristic honey-colored crust. Non-bullous impetigo is often seen around the nose and mouth.
- Bullous Impetigo: Less common than non-bullous impetigo, this type is characterized by larger fluid-filled blisters. The blisters are more stable and less likely to rupture than in the non-bullous form. Bullous impetigo often affects the trunk, buttocks, and limbs.
- Ecthyma: This is a more severe and deeper form of impetigo. It extends into the deeper layers of the skin, causing painful, ulcerative sores. Ecthyma is more likely to result in scarring and may leave permanent marks on the skin.
Contact to know more
Contact
Powai: 52, Galleria Mall,
Central Avenue, Hiranandani Gardens,
Powai, Mumbai-400076
Mobile Number: 08291492566
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
