Lichen Planus
Lichen Planus: Unraveling Symptoms, Causes, and Types
Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can affect various parts of the body, mucous membranes, and nails. It is characterized by the development of flat-topped, itchy, and often polygonal-shaped papules or lesions. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of lichen planus is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Symptoms:
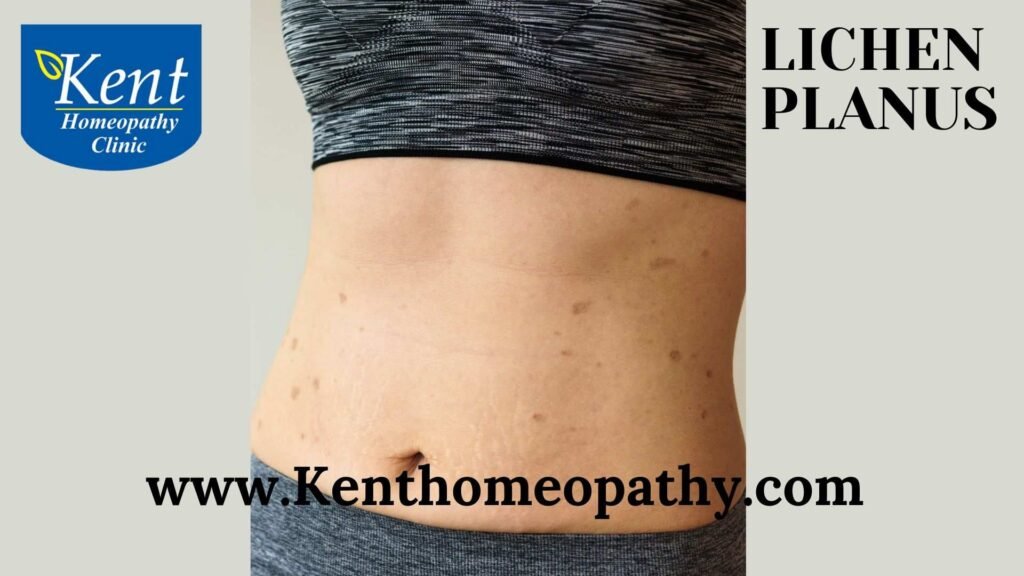
- Skin Lesions: The hallmark symptom of lichen planus is the presence of skin lesions. These lesions are typically purplish, flat-topped bumps that may have a shiny surface. They can vary in size and shape, and when grouped, they often form a pattern resembling lace.
- Itching: Lichen planus is often accompanied by intense itching, which can range from mild to severe. The itching can significantly impact the affected individual’s quality of life.
- Nail Changes: In some cases, lichen planus can affect the nails, leading to changes such as ridges, grooves, or pitting. The nails may become thin or brittle.
- Oral Lesions: Lichen planus can involve the mucous membranes, particularly in the mouth. Oral lesions may present as white, lacy patches, ulcers, or red, swollen areas.
- Scalp Involvement: Lichen planus can affect the scalp, leading to redness, itching, and the development of lesions. Hair loss may occur in the affected areas.
- Genital Involvement: Genital lichen planus can cause lesions on the genital skin, leading to discomfort, pain, or itching.
- Hyperpigmentation or Hypopigmentation: As lichen planus lesions heal, they may leave behind areas of hyperpigmentation (darkened skin) or hypopigmentation (lightened skin).
- Koebner Phenomenon: Some individuals with lichen planus may experience the Koebner phenomenon, where new lesions develop at sites of skin trauma or injury.
Causes:
The exact cause of lichen planus is not well understood, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response. Potential triggers and factors associated with lichen planus include:
- Autoimmune Response: Lichen planus is thought to be an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, leading to inflammation and the development of lesions.
- Genetic Predisposition: There may be a genetic component, as lichen planus sometimes occurs in families. Certain genetic factors may contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to the condition.
- Viral Infections: Some viral infections, including hepatitis C, may be associated with the development or exacerbation of lichen planus in susceptible individuals.
- Stress: While not a direct cause, stress and emotional factors may play a role in triggering or exacerbating lichen planus in some individuals.
- Contact Allergens: Exposure to certain chemicals or allergens may contribute to the development of lichen planus, especially in the oral or genital areas.
- Dental Restorations: Dental materials, particularly dental amalgam, have been suggested as potential triggers for oral lichen planus in some individuals.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during menopause, may influence the development of lichen planus, especially in the genital area.
Types:
- Classic Lichen Planus: This is the most common form, characterized by the development of skin lesions on various parts of the body.
- Oral Lichen Planus: Involves the mucous membranes of the mouth and can present as white, lacy patches, red areas, or ulcers. It may cause discomfort or pain while eating or speaking.
- Genital Lichen Planus: Affects the genital area and can lead to lesions on the vulva, vagina, penis, or scrotum. It may cause itching, pain, or discomfort.
- Nail Lichen Planus: Involves the nails, leading to changes such as ridges, grooves, pitting, thinning, or brittleness.
- Scalp Lichen Planus: Affects the scalp and may cause redness, itching, and the development of lesions. Hair loss (scarring alopecia) may occur in severe cases.
- Linear Lichen Planus: Presents as lesions arranged in a linear or band-like pattern on the skin. This form may follow the lines of trauma or injury.
- Hypertrophic Lichen Planus: Characterized by thickened, raised lesions that may resemble keloids. This variant is less common but can be more resistant to treatment.
- Actinic Lichen Planus: Aggravated by sun exposure, this variant is more commonly seen in sun-exposed areas of the skin and may have hypertrophic features.
Contact to know more
Contact
Powai: 52, Galleria Mall,
Central Avenue, Hiranandani Gardens,
Powai, Mumbai-400076
Mobile Number: 08291492566
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
