Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Types
Mastoiditis is a bacterial infection of the mastoid bone, a prominent bone behind the ear. It often develops as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated middle ear infections (otitis media). Mastoiditis can lead to inflammation, pain, and potential complications, making prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment essential.
Symptoms:
- Ear Pain:
– Persistent or severe ear pain is a common symptom, often localized to the affected ear.
- Ear Discharge:
– Pus or other discharge from the ear may be present, indicating an infection in the middle ear.
- Hearing Loss:
– Hearing loss can occur due to the inflammation and infection affecting the structures of the ear.
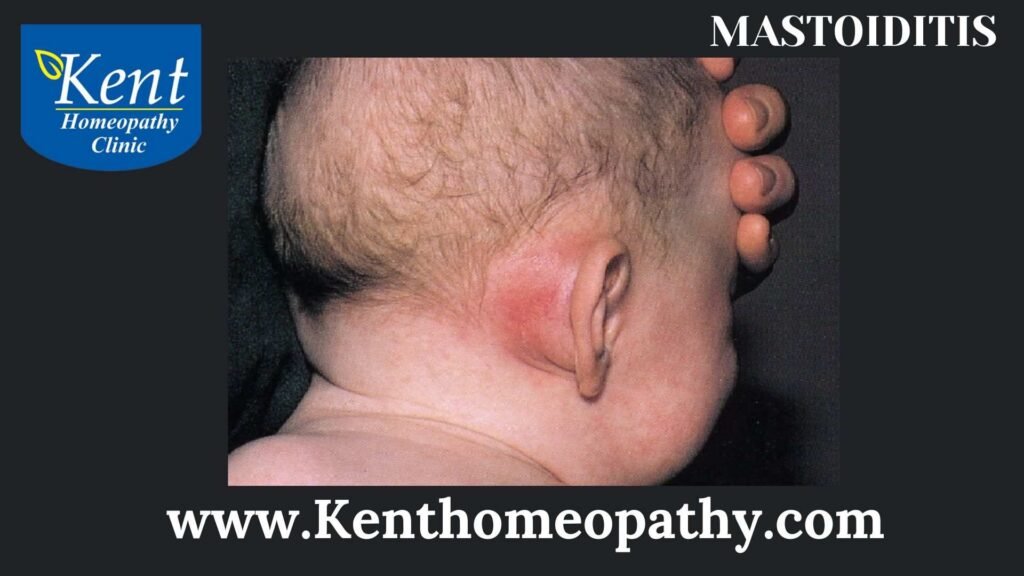
- Swelling Behind the Ear:
– Swelling and redness may be visible behind the affected ear, where the mastoid bone is located.
- Fever:
– Elevated body temperature, fever, is a typical response to infection.
- Headache:
– Headaches, particularly localized around the affected ear, may occur.
- Fatigue:
– Generalized weakness and fatigue are common symptoms, reflecting the body’s response to infection.
- Irritability (in children):
– Children with mastoiditis may exhibit irritability, fussiness, or difficulty sleeping.
Causes:
- Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media):
– Mastoiditis often arises as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated middle ear infections. Bacteria from the middle ear can spread to the mastoid bone.
- Blockage of the Eustachian Tube:
– The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the nose. Blockage of this tube can trap bacteria in the middle ear, leading to infection and potential spread to the mastoid.
- Respiratory Infections:
– Infections such as respiratory tract infections or colds can contribute to the development of middle ear infections and, subsequently, mastoiditis.
- Immunocompromised State:
– Individuals with compromised immune systems, due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or certain medical treatments, may be more susceptible to mastoiditis.
Types of Mastoiditis:
- Acute Mastoiditis:
– This is the initial stage of infection, characterized by rapid onset of symptoms. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
- Subacute Mastoiditis:
– If acute mastoiditis is not promptly treated, the infection may progress to a subacute stage with persistent symptoms and a greater risk of complications.
- Chronic Mastoiditis:
– Long-term or recurrent infections may lead to chronic mastoiditis, marked by ongoing inflammation and potential damage to the mastoid bone and surrounding structures.
- Complicated Mastoiditis:
– Complications can arise if the infection spreads to nearby structures, such as the inner ear, facial nerve, or brain. This can result in more severe symptoms and potential life-threatening complications.
It’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms of mastoiditis, such as ear pain, discharge, or swelling, are present. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment help prevent the progression of the infection and reduce the risk of complications. Parents should be particularly vigilant about recognizing signs of ear infections in children to initiate timely intervention.
In conclusion, mastoiditis is a potentially serious condition that can result from untreated middle ear infections. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and types is essential for early detection and appropriate management. With prompt medical intervention, including antibiotic therapy and, if necessary, surgical procedures, the majority of individuals with mastoiditis can achieve a full recovery.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
