Non-healing ulcers
Non-Healing Ulcers: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Types
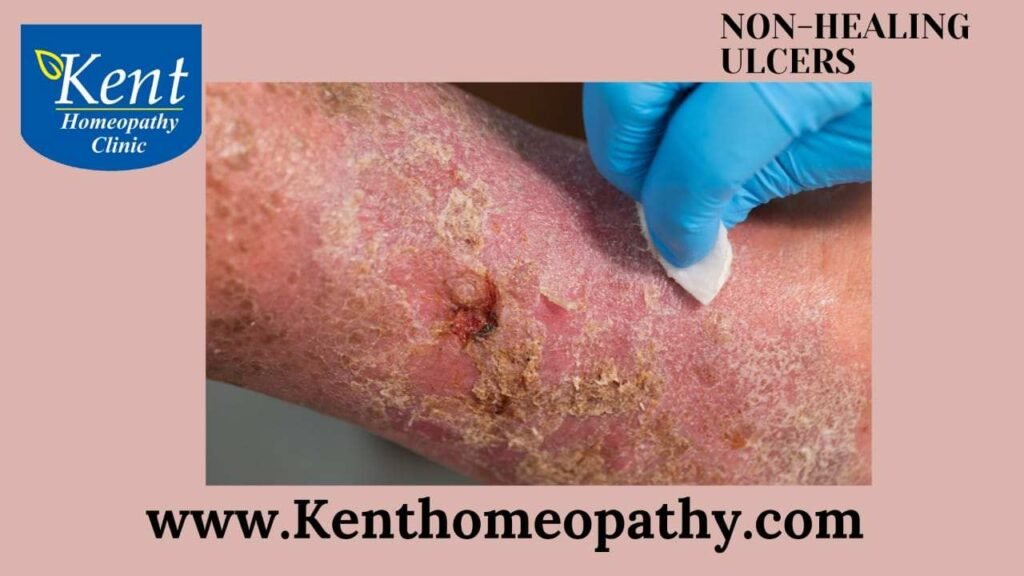
Non-healing ulcers are chronic wounds that fail to progress through the normal phases of healing within an expected timeframe. These ulcers can be persistent, leading to complications and posing challenges in their management. Key aspects of non-healing ulcers, including symptoms, causes, and types, are essential to address for effective treatment.
Symptoms:
The hallmark symptom of non-healing ulcers is the persistence of an open wound without signs of improvement. Other common symptoms include:
- Prolonged Wound Presence: The primary indicator is the continued existence of the ulcer without significant healing progress.
- Pain or Discomfort: Non-healing ulcers can be associated with pain or discomfort, which may vary in intensity.
- Inflammation: Redness and swelling around the ulcer site may indicate ongoing inflammation, potentially caused by infection or impaired healing.
- Odor: In some cases, non-healing ulcers may produce an unpleasant odor, often associated with infection or necrotic tissue.
Causes:
Several factors contribute to the development of non-healing ulcers, and the underlying cause can vary. Common causes include:
- Poor Blood Circulation: Inadequate blood flow to the affected area, often due to conditions like peripheral artery disease, can impede the healing process.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are prone to develop ulcers, particularly on the feet, due to nerve damage and poor circulation.
- Infection: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections can hinder wound healing, leading to chronic ulcers.
- Pressure Ulcers: Prolonged pressure on a specific area, commonly seen in bedridden individuals, can result in non-healing ulcers known as pressure ulcers or bedsores.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like vasculitis or lupus can cause inflammation in blood vessels, affecting proper wound healing.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate nutrition can compromise the body’s ability to repair and regenerate tissues, contributing to non-healing ulcers.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic illnesses such as HIV, certain cancers, or autoimmune disorders may impede the healing process.
- Venous Insufficiency: Poor functioning of the venous valves can lead to chronic venous ulcers, often seen in the lower legs.
Types:
- Arterial Ulcers:
– Causes: Insufficient blood flow due to arterial disease, atherosclerosis, or peripheral artery disease.
– Location: Commonly found on the lower extremities, especially toes or heels.
– Characteristics: Painful, with well-defined edges and minimal exudate.
- Venous Ulcers:
– Causes: Poor venous circulation, often associated with chronic venous insufficiency.
– Location: Typically on the lower legs, near the ankles.
– Characteristics: Edges are irregular, and ulcers may have moderate to high exudate.
- Pressure Ulcers (Bedsores):
– Causes: Prolonged pressure on specific areas, commonly in bedridden or immobile individuals.
– Location: Bony prominences like the hips, heels, or sacrum.
– Characteristics: Varying stages of severity, from superficial to deep wounds.
- Diabetic Ulcers:
– Causes: Neuropathy, poor circulation, and impaired immune function in individuals with diabetes.
– Location: Often on the feet, especially pressure points.
– Characteristics: May be painless initially, with potential for infection.
- Neuropathic Ulcers:
– Causes: Nerve damage, often associated with conditions like diabetes.
– Location: Areas subjected to repetitive trauma or pressure.
– Characteristics: Lack of pain due to nerve damage, may have irregular edges.
Addressing the underlying cause is crucial for the effective treatment of non-healing ulcers. A comprehensive approach involving wound care, infection management, and addressing contributing factors such as circulation or nutritional issues is essential for successful ulcer healing. Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach with healthcare professionals are key in managing non-healing ulcers.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
