Rheumatism
Rheumatism: Unraveling Symptoms, Causes, and Types
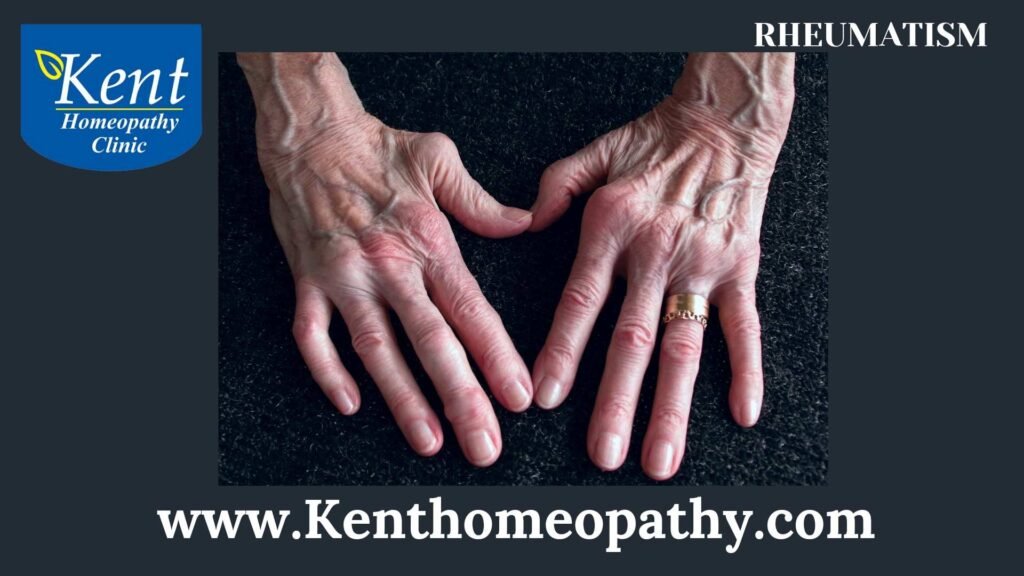
Rheumatism is a term historically used to describe various disorders affecting the joints, muscles, and connective tissues. Over time, the term has become less specific, and many conditions that were once labeled as rheumatism are now identified and categorized more precisely. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types associated with what was traditionally referred to as rheumatism is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Symptoms:
- Joint Pain:
– Joint pain is a common symptom of rheumatism. It can affect multiple joints simultaneously and may vary in intensity.
- Stiffness:
– Stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking in the morning, is a characteristic symptom. Stiff joints can limit mobility.
- Swelling:
– Swelling of the joints may occur, contributing to pain and reduced joint function.
- Warmth and Redness:
– Inflammation in the affected joints can lead to warmth and redness in the surrounding areas.
- Fatigue:
– Chronic fatigue is often associated with rheumatism. The overall feeling of tiredness can impact daily activities.
- Muscle Pain:
– In addition to joint pain, rheumatism may involve muscle pain, especially in conditions affecting both joints and muscles.
- Limited Range of Motion:
– Rheumatism can result in a limited range of motion in affected joints, making it difficult to perform certain movements.
Causes:
- Autoimmune Factors:
– Autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, can lead to rheumatic conditions. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Inflammatory Responses:
– Inflammation plays a significant role in many rheumatic conditions. Abnormal inflammatory responses contribute to joint and tissue damage.
- Genetic Predisposition:
– Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to rheumatic diseases, making them more susceptible to developing these conditions.
- Environmental Factors:
– Environmental factors, such as exposure to certain infections or toxins, may contribute to the development or exacerbation of rheumatic conditions.
- Age and Gender:
– Rheumatic conditions often have a higher prevalence in older individuals, and some are more common in a particular gender. For example, rheumatoid arthritis is more prevalent in women.
- Hormonal Influences:
– Hormonal changes, especially in women, can impact the onset and severity of certain rheumatic conditions.
Types:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA):
– Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by inflammation of the synovium, the lining of the joints. It commonly affects the small joints in the hands and feet, leading to pain, swelling, and joint deformities.
- Osteoarthritis (OA):
– Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the protective cartilage on the ends of bones wears down over time. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE):
– Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect various organs, including the joints. Joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are common symptoms.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis:
– Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects the spine, causing pain and stiffness. It can also affect other joints and organs.
- Gout:
– Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in the joints. It often affects the big toe and can cause sudden, severe pain and swelling.
- Fibromyalgia:
– Fibromyalgia is characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in specific areas. It is not an inflammatory condition but is often associated with rheumatic symptoms.
- Psoriatic Arthritis:
– Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis that can affect individuals with psoriasis. It causes joint pain, swelling, and skin changes.
- Sjögren’s Syndrome:
– Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the glands producing saliva and tears. Joint pain and stiffness are common in individuals with this condition.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
