Tinea alba
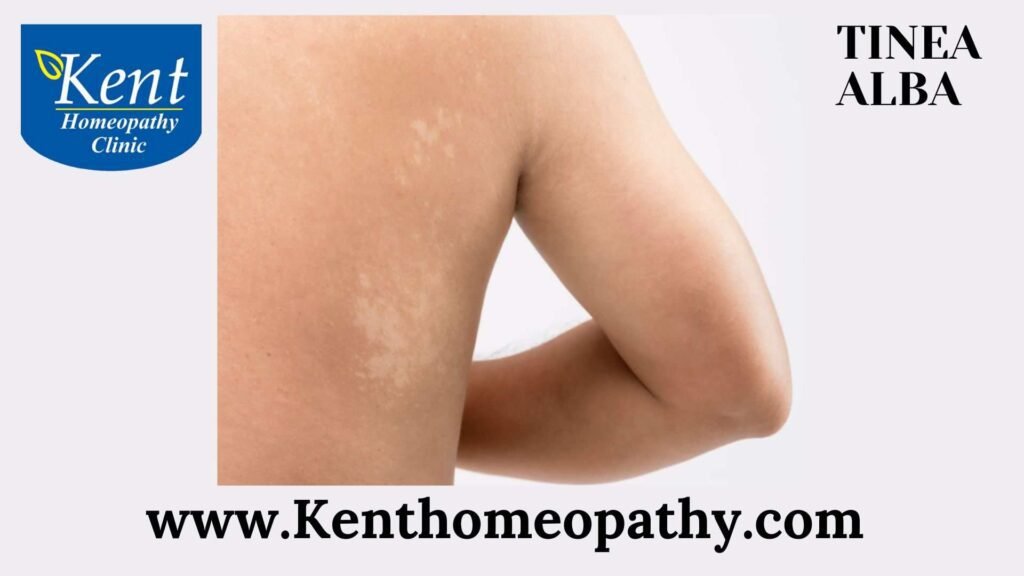
Tinea Alba: Decoding Symptoms, Causes, and Types
Tinea alba is a common skin condition that typically affects children and adolescents. It is a type of superficial fungal infection that manifests as dry, hypopigmented, scaly patches on the skin. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and types of tinea alba is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Symptoms:
- Hypopigmented Patches:
– The primary symptom of tinea alba is the presence of light-colored, hypopigmented patches on the skin. These patches may be round or oval and are usually lighter than the surrounding skin.
- Dry and Scaly Skin:
– Tinea alba often presents with dry and scaly skin on the affected patches. The skin may appear flaky, giving it a texture that is different from the surrounding normal skin.
- Mild Itching:
– Itching is a common symptom, but it is usually mild. Individuals with tinea alba may experience occasional itching on the affected areas.
- Circular or Oval Shape:
– The patches of tinea alba are often circular or oval in shape. They may vary in size and can occur on different parts of the body.
- Face, Neck, and Upper Arms:
– Tinea alba commonly occurs on the face, particularly the cheeks, neck, and upper arms. However, it can also affect other areas of the body.
Causes:
- Fungal Infection (Tinea):
– Tinea alba is caused by a superficial fungal infection. The specific fungus involved is often a type of dermatophyte, such as Trichophyton or Microsporum.
- Predisposing Factors:
– Certain factors predispose individuals to tinea alba, including a warm and humid climate, excessive sweating, and sharing personal items like towels or clothing.
- Atopy (Genetic Predisposition):
– Individuals with a genetic predisposition to atopic conditions, such as eczema or asthma, may be more prone to developing tinea alba.
- Weakened Immune System:
– A compromised immune system can increase the risk of fungal infections, including tinea alba. This may be seen in individuals with conditions like HIV or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy.
- Poor Hygiene Practices:
– Poor hygiene practices, especially in warm and humid conditions, can contribute to the development and spread of fungal infections.
- Excessive Sun Exposure:
– Sun exposure can exacerbate the hypopigmentation associated with tinea alba, making the affected patches more noticeable.
Types:
- Tinea Versicolor:
– Tinea versicolor is a type of fungal infection caused by the yeast Malassezia. It typically presents as discolored patches on the skin, which can be either lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. While tinea versicolor is distinct from tinea alba, they share some similarities.
- Tinea Corporis (Ringworm):
– Tinea corporis, commonly known as ringworm, is a fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body, including the face, neck, and arms. It may present as red, circular, and scaly patches, sometimes with an elevated border.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema):
– Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and itching. While eczema is not a fungal infection, its appearance can be similar to tinea alba, especially during flares.
Contact to know more
Contact
Timings
Monday to Saturday:
11:00 AM to 02:30 PM
06:30 PM to 09:00 PM
